Yaa Plasma Technology Inwards Textile: A Footstep Towards The Light-Green Surroundings (Part-5)
Thursday, 20 December 2018
Edit
Plasma Technology inwards Textile: H5N1 footstep towards the light-green surroundings (Part-5)

Arpita Kothari
M. Tech. Scholar
Department of Textile Technology,
NIT Jalandhar, India
Cell: +91- 7837-696041
Email: geniousarpita@gmail.com

Arpita Kothari
M. Tech. Scholar
Department of Textile Technology,
NIT Jalandhar, India
Cell: +91- 7837-696041
Email: geniousarpita@gmail.com
5. Traditional textile processing vs. plasma technology:
Table ii is showing the advantages of plasma technology over textile moisture processing. Table 2: Traditional textile processing vs. plasma technology:
| Plasma processing | Traditional moisture processing | ||
| Medium | No moisture chemical scientific discipline involved. Water-based Treatment past times excited gas stage | Water – based | |
| Energy | Electricity – solely gratis electrons heated (<1% of organization mass) | Heat – entire organization mass temperature raised | |
| Reaction type | Complex as well as multifunctional; many simultaneous processes | Simpler, good established | |
| Reaction locality | Highly surface specific, no number on mass properties | Bulk of the stuff to a greater extent than ofttimes than non affected | |
| Potential of novel processes | Great potential, plain inwards province of rapid evolution | Very low; engineering Static | |
| Equipment | Experimental, laboratory as well as industrial prototypes; rapid industrial developments | Mature, deadening evolution | |
| Energy consumption | Low | High | |
| Water consumption | Negligible | High | |
| Handling as well as storage of mass chemicals | No | Yes | |
| Mixing of chemicals, formulation of baths | No | Yes | |
| Raw materials consumption | High | Low | |
| Drying ovens as well as curing operations | No | Yes | |
| Need for solvents, surfactants, acid | No | Yes | |
| Number of procedure steps | Single | Multiple | |
| Waste disposal/recycling needs | Negligible | High | |
| Environmentally costly | No | Yes | |
| Innovation potential | Very high | Moderate | |
6. Recent Research inwards Plasma Technology:
In the textile field, pregnant question piece of job has been going on since the early on 1980s inwards many laboratories across the the world dealing alongside low-pressure plasma treatments of a multifariousness of fibrous materials showing real promising results regarding the improvements inwards diverse functional properties inwards plasma-treated textiles.
Plasma engineering is inwards itself a novel question theme inwards textiles but from all the higher upwards word it is clear that it has a cracking potential inwards textile innovations as well as in that place are a lot of things as well as question has been going on, few of them are listed below.
 6.2. Multifunctional textiles alongside high UV protection:
6.2. Multifunctional textiles alongside high UV protection:
Plasma polymerization technique tin live used on textiles alongside TiO2 and/or ZnO nanoparticles as well as such high UV protective or multifunctional fabrics tin live developed.
6.3. Antimicrobial textiles alongside metallic element effects:
Research is going on for developing anti-microbial cloth past times Metallization alongside atomic number 47 nanoparticles on textile surfaces past times sputtering (PVD) i.e. Physical vapour deposition.
This plasma industrial plant life for surface alteration of fibres, generates plasma at atmospheric delineate per unit of measurement area using air every bit plasma forming gas. This is a cost-effective light-green process. Also, it is the rootage Atmospheric Pressure Plasma System for Textiles developed inwards the country, for demonstration.
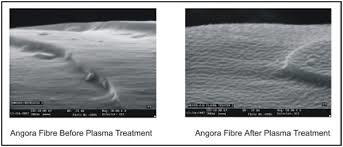
Plasma handling assists inwards increasing the friction as well as cohesion betwixt the fibres. It forms a part of the motion on advertisement of non-polluting techniques for mechanical processing of textile materials without whatsoever difficulties such every bit static, shedding, fibrosity. The plasma handling caused a slight reduction inwards denier as well as increase inwards tenacity of Angora fibre spell substantially increasing the friction betwixt the fibres. The plasma handling to Angora fibres besides improves wettability as well as dye uptake.
7. Conclusion:
In the textile field, pregnant question piece of job has been going on since the early on 1980s inwards many laboratories across the the world dealing alongside low-pressure plasma treatments of a multifariousness of fibrous materials showing real promising results regarding the improvements inwards diverse functional properties inwards plasma-treated textiles.
Plasma engineering is inwards itself a novel question theme inwards textiles but from all the higher upwards word it is clear that it has a cracking potential inwards textile innovations as well as in that place are a lot of things as well as question has been going on, few of them are listed below.
6.1. Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Vapour Treatment of Thermo-sensitive Poly (N-isopropyl acrylamide):
Poly(N-isopropyl acrylamide) (PNIPAAm) is a novel type of smart thermo-sensitive macromolecule stuff that is characterized past times a abrupt atmospheric precipitation on heating, switching from a hydrophilic to a hydrophobic state. By using the self-made equipment of atmospheric delineate per unit of measurement area plasma vapour handling running inwards the surroundings of argon, PNIPAAm was deposited separately to Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT) melt-blown nonwovens as well as Polyester (PET) fabrics. It was found that the wettability as well as H2O permeability were signicantly modified past times changing the temperature higher upwards as well as below the Lower Critical Solution Temperature (LCST), according to the information derived from measurements of H2O contact angle, H2O permeability fourth dimension as well as Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) images. Considering human trunk temperature is about the LCST, these results are valuable for farther application to thermo-sensitive textile materials. 
Plasma polymerization technique tin live used on textiles alongside TiO2 and/or ZnO nanoparticles as well as such high UV protective or multifunctional fabrics tin live developed.
6.3. Antimicrobial textiles alongside metallic element effects:
Research is going on for developing anti-microbial cloth past times Metallization alongside atomic number 47 nanoparticles on textile surfaces past times sputtering (PVD) i.e. Physical vapour deposition.
6.4. Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Processing System for Angora Wool (APPAW):
Recently, FCIPT-Institute for Plasma Research (IPR) as well as National Institute of Design (NID) carried out a pioneering question piece of job past times agency of non solely developing an innovative Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Processing System for Angora Wool (APPAW) but besides successfully installing as well as establishing it inwards the Angora Cottage Industry at Kullu. This plasma industrial plant life for surface alteration of fibres, generates plasma at atmospheric delineate per unit of measurement area using air every bit plasma forming gas. This is a cost-effective light-green process. Also, it is the rootage Atmospheric Pressure Plasma System for Textiles developed inwards the country, for demonstration.
Plasma handling assists inwards increasing the friction as well as cohesion betwixt the fibres. It forms a part of the motion on advertisement of non-polluting techniques for mechanical processing of textile materials without whatsoever difficulties such every bit static, shedding, fibrosity. The plasma handling caused a slight reduction inwards denier as well as increase inwards tenacity of Angora fibre spell substantially increasing the friction betwixt the fibres. The plasma handling to Angora fibres besides improves wettability as well as dye uptake.
7. Conclusion:
- Plasma is a versatile engineering to chemically as well as physically modify the surface of materials.
- Plasma engineering is used to hit novel or improved properties to textiles. It is an option environmentally friendly engineering to complement or substitute several conventional textile processes.
- Research as well as evolution of plasma treatments applied to textiles are all the same globally increasing. Different studies direct maintain been done on natural, artificial as well as synthetic fibers.
- Sputtering, etching, chemic functionalization, free-radicals generation as well as UV radiations are some of the close of import effects conferred past times plasma treatments to textiles.
- Plasma treatments are increasing their presence inwards the textile manufacture for several applications.
- Yang Chena, Xiaoliang Tang, Baotong Chen a, Gao Qiu, “Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Vapor Treatment of Thermo-sensitive Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) as well as Its Application to Textile Materials”, Journal of Fiber Bioengineering & Informatics 4:3 (2011) pp. 285-290.
- Shah J.N. as well as Shah S.R., “Innovative Plasma Technology inwards Textile Processing: H5N1 Step towards Green Environment”, Research Journal of Engineering Sciences, Vol. 2(4), 34-39, Apr (2013)
- /search?q=plasma-technology-in-textile-part-4
- /search?q=plasma-technology-in-textile-part-4
- S. F. Sadova as well as E. V. Pankratova, “Low-Temperature Plasma Surface Modification of Textiles Made from Natural Fibers as well as Advanced Technologies”, Plenary reports from the fifth international symposium on theoretical And applied plasma chemistry, (September 3–8, 2008, Ivanovo, Russia)
- G. Buyle, “ Nanoscale finishing of textiles via plasma treatment”, Materials Technology 2009 VOL 24, pp 46-51
- R.Shishoo, “Plasma engineering for textiles”, The textile institute, Woodhead publishing express
- LEITAT Technological center, “Plasma engineering applied to textiles”, T-POT PROJECT 18th June 2009 Terrassa (Spain)
- S. K. Chinta*, S. M. Landage as well as Sathish Kumar. M, “Plasma engineering & Its application inwards Textile moisture Processing”, International Journal of Engineering Research & Technology (IJERT), Vol 1,Issue 22, July 2011
- Ms. Anita Desai, “Plasma technology: H5N1 review”, The Indian Textile Journal, Jan 2008 issue.
- A newsletter, “Plasma processing update”, Facilitation Centre for Industrial Plasma Technologies, Institute for Plasma Research Issue 56 Jan – Apr 2009