Now You Know Knitting Action of Spring Bearded Needle
Tuesday, 22 January 2019
Edit
Knitting Action of Spring Bearded Needle
Rofiquzzaman Raju
Fabric Technologist,
B.J.Group, Mawna, Gazipur
Chittagong Textile Engineering College
Contact: 01714419681
Fabric Technologist,
B.J.Group, Mawna, Gazipur
Chittagong Textile Engineering College
Contact: 01714419681
Introduction:
Spring bearded needle was the first type of needle to be produced. It is the cheapest and simplest type to manufacture as it is made from a single piece of metal. Loop or stitch formation on a single needle bed weft knitting machine with spring bearded needles consists of the following stages:
- Yarn feeding
- Yarn sinking or kinking
- Under lapping
- Pressing
- Landing
- Joining and casting-off
- Clearing
The essence of these stages consist in the following operations:
1. Yarn feeding: The newly fed yarn is laid under the throats of kinking sinkers.
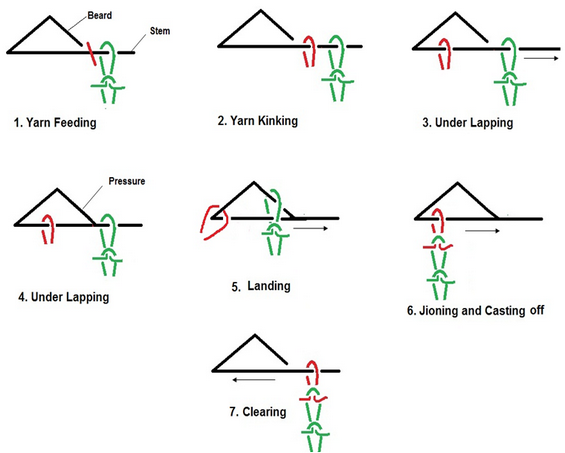 |
| Fig: Knitting action or knitting cycle on spring-bearded needles |
2. Yarn sinking: The sinkers fall down between the needles, with the yarn held in the Sinker throats. Depth of sinking determines the loop length, i.e, the yarn length used to form a knitted loop.
3. Under lapping: The yarn laid on the needle stems is withdrawn by the sinkers in direction of needle hooks and under the needle beards.
4. Pressing: Now, the needle beard is immersed in the needle groove by a presser disc. In this way the fed yarn is closed in the needle hook.
5. Landing: The knitted fabric resting on the needle stems at the needle bed is now pushed by cast-off sinkers towards the pressed needle beards, and the fabric loops (called old loops) land on the beards.
6. Joining and Casting-off: After passing the presser disc, the cast-off sinkers push further the knitted fabric towards the tips of the needles. At the same time the kinking sinkers leave the kinked yarn and the cast-off sinkers push the old loops off the needles on to the kinked lengths of yarn.
7. Clearing: At this stage the newly formed loops are pushed back along the needle stems, towards the needle bed; the knitted fabric enlarged by a new course of knitted loops, is drawn down by means of a take-down mechanism, and the process of loop formation may be started again.