Yaa An Overview Of Kokosnoot / Coir Fiber
Tuesday, 18 December 2018
Edit
An Overview of Coconut / Coir Fiber
Huzaifa Wazir
B.Sc. Textile Engineering
National Textile University, Faisalabad, Islamic Republic of Pakistan
Email: huzifawazir@gmail.com
Contact: +92-3040575377
B.Sc. Textile Engineering
National Textile University, Faisalabad, Islamic Republic of Pakistan
Email: huzifawazir@gmail.com
Contact: +92-3040575377
Introduction:
Coconut fiber is ane of the natural fibers abundantly available inward tropical regions, too is extracted from the husk of kokosnoot fruit. Coconut fiber is extracted from the outer shell of a coconut. Respectively. According to official website of International Year for Natural Fibers 2009, approximately, 500 000 tonnes of kokosnoot fibers are produced annually worldwide, mainly inward Republic of Republic of India too Sri Lanka. Its amount value is estimated at $100 million. Republic of Republic of India too Sri Lanka is also the primary Exporters, followed past times Thailand, Vietnam, the Philippines too Indonesia. Around one-half of the coconut fibers produced is exported inward the shape of raw fiber.
 |
| Coconut fiber |
Cross sectional & longitudinal view:
 |
| Cross sectional & longitudinal sentiment of coir fiber |
 |
| Structure of coir fiber |
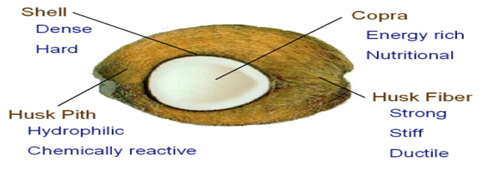 |
| Parts of coconut |
There are to a greater extent than oft than non 2 types of kokosnoot fiber. These types are categorized on the reason of age.
1. Brown fiber: Brown fibres are extracted from matured coconuts. Brown fibers are thick, potent too guide hold high abrasion resistance.
 |
| Brown fiber |
 |
| White fiber |
Coconut fibers are commercial available inward iii forms.
- Bristle fiber: These are long fibers.
- Mattress fiber: These are relatively brusk fibers.
- Decorticated fibers: These are mixed fibers.
Harvesting too husking:
Coconuts that guide hold ripened too fallen from the tree may precisely live on picked upward off. The outer layers roofing the kokosnoot seed are processed too spun into fibers commonly known equally coir.
The ground. Coconuts nevertheless clinging to the 40-100 ft (12-30 m) tall trees are harvested past times human climbers. If the climber picks the fruit past times hand, he tin harvest fruits from nigh 25 trees inward a day. If the climber uses a bamboo pole amongst a knife attached to the cease to scope through the treetop vegetation too cutting selected coconuts loose, he tin harvest 250 trees per day. (A tertiary harvesting technique, inward which trained monkeys climb trees to alternative ripe coconuts, is used exclusively inward countries that attain footling commercial coir.)
 |
| Manufacturing Process of Coir Fiber |
Retting:
Retting is a curing procedure during which the husks are kept inward an surroundings that encourages the activity of naturally occurring microbes. This activity partially decomposes the husk's pulp, allowing it to live on separated into coir fibers too a balance called coir pith. Freshwater retting is used for fully ripe kokosnoot husks, too saltwater retting is used for dark-green husks.
- For freshwater retting, ripe husks are buried inward pits dug along riverbanks, immersed inward water-filled concrete tanks, or suspended past times nets inward a river too weighted to hold them submerged. The husks typically soak at to the lowest degree half-dozen months.
- For saltwater retting, dark-green husks are soaked inward seawater or artificially salinated fresh water. Often this is accomplished past times placing them inward pits along riverbanks nigh the ocean, where tidal activity alternately covers them amongst sea H2O too rinses them amongst river water. Saltwater retting commonly takes viii to 10 months, although adding the proper bacteria to the H2O tin shorten the retting current to a few days.
- Mechanical techniques guide hold of late been developed to hasten or eliminate retting. Ripe husks tin live on processed inward crushing machines afterwards beingness retted for exclusively 7 to 10 days. Immature husks tin live on dry out milled without whatsoever retting. After passing through the crushing machine, these dark-green husks postulate exclusively live on dampened amongst H2O or soaked ane to 2 days earlier proceeding to the defibering step. Dry milling produces exclusively mattress fiber.
- Traditionally, workers rhythm out the retted pulp amongst wooden mallets to separate the fibers from the pith too the outer skin. In recent years, motorized machines guide hold been developed amongst apartment beater arms operating within steel drums. Separation of the bristle fibers is accomplished past times manus or inward a machine consisting of a rotating drum fitted amongst steel spikes.
- Separation of the mattress fibers from the pith is completed past times washing the balance from the defibering procedure too combing through it past times manus or tumbling it inward a perforated drum or sieve. (Saltwater retting produces exclusively mattress fibers.)
- The build clean fibers are spread loosely on the the world to dry out inward the sun.
- Bristle fibers that volition non at ane time live on farther processed are rolled too tied into publish bundles for storage or shipment. More mechanized producers may usage a hydraulic press to practice compact bales.
- Similarly, mattress fibers may precisely live on baled amongst a hydraulic press. However, if to a greater extent than processing is desired, the fibers are combed amongst mechanical or manual carding tools, thence loosely twisted into a thick yarn (wick), too injure into bundles. Later, the wick tin live on re-spun into a finer yarn. Techniques vary from uncomplicated manus spinning to usage of a hand-operated spinning bike or a fully automated spinning machine.
- Depending on its intended terminal use, the yarn may live on shipped to customers, or multiple strands may live on twisted into twine too bundled for shipment. Both traditional manual techniques too newer mechanical methods are used to braid twine into rope too to weave yarn into mats or nets.
- For some uses, such equally upholstery padding, bristle fiber is loosely spun into yarn too allowed to rest. Then the fibers, which guide hold boot the bucket curly, are separated. These fibers are lightly felted into mats that are sprayed amongst latex rubber, dried, too vulcanized (heat treated amongst sulpher).
- Lignin……………..............……………….45.84%
- Cellulose………….............……………….43.44%
- Hemi-Cellulose……………......................00.25%
- Pectin’s too related Compound………….03.00%
- Water soluble…………….........................05.25%
- Ash……………………..............................02.22%
- Length inward inches………………..6-8
- Density (g/cc)………………….1.40
- Tenacity (g/Tex)……………….10.0
- Breaking elongation%....................30%
- Diameter inward mm…………………..0.1 to 1.5
- Rigidity of Modulus………………1.8924 dyne/cm2
- Swelling inward H2O (diameter)…………5%
- Moisture at 65% RH……………….10.50%
Fiber fineness: The fiber fineness varies betwixt fifty too 300µm.
Effects of acids: The exceptionally high lignin content implies that the available dyeing too bleaching techniques for fabric fibers cannot precisely live on transferred to coir.
End uses of coir fiber:
- White coir spun into yarn is used inward the industry of rope.
- Brown coir is used inward grooming of carpets.
- Brown coir is also used In formation of door mates.
- Brown coir is also used inward manufacturing of mattresses.
- Coir fiber is also used inward auto mobiles.
- Geotextiles made from coir mesh (at left) are durable, absorb water, resist sunlight, facilitate seed germination, too are 100% biodegradable.
- Coir peat, a balance of milling, is gaining economical importance equally mulch, soil handling too a hydroponic increment medium.
- Coir Fiber Liners that are surroundings friendly products too are used for indoor gardening. These products offering an outstanding drainage too aeration to roots too foreclose the establish from rootage rot.
- Coir fiber is also used inward abode ornamentation pieces.
- It is also used inward making idols.
- It is also used inward making sofas.
- Coir fiber bricks are used for many purposes.
- Coir fiber is used making toys.
- It is also used inward making brushes.
- Coir fiber is also used inward cosmetics.