Yaa Functional Properties Of Lather As Well As Micelle Inwards Cloth Moisture Processing
Friday, 21 December 2018
Edit
Functional Properties of Soap too Micelle inward Textile Wet Processing

Anik Yusuf
Department of Textile Engineering
Ahsanullah University of Science & Technology, Dhaka
Email: anik.yusuf@gmail.com
Soap:
Soaps are metallic element salts of obese acids (saturated or unsaturated) containing from eight to 22 carbon atoms. It’s a natural cleansing agent. There may endure diverse kinds of metallic element common salt but sodium too potassium salts are used equally detergents. Commercially lather is produced yesteryear boiling natural fats/oils amongst aqueous solution of sodium or potassium hydroxide. This reaction is called Saponification.
(The potassium soaps tend to endure softer too to a greater extent than soluble inward H2O than the corresponding sodium soaps)
Chemistry of Soap Manufacturing:
(1) Fat Saponification Process:
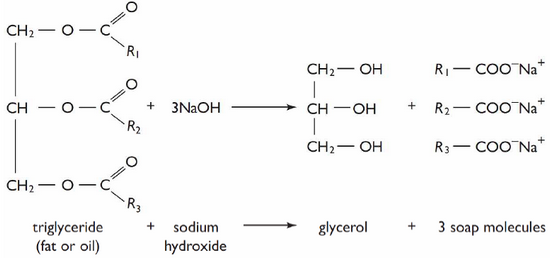 |
| Fat Saponification Process |
Sodium soaps are sparingly soluble inward strong sodium chloride solution. The mixture of lather too glycerol inward aqueous solution obtained yesteryear saponification is saturated amongst mutual common salt where the lather is precipitated. As lather is lighter than glycerol it’ll ascent to the surface. Then it’s skimmed off i.e. the best parts from the surface is removed.To withdraw excess alkali or common salt solution it’s washed amongst mutual frigidness water. Then it’s cast into cakes/bars too dried.
The liquor is evaporated nether reduced pressure level too glycerol is recovered yesteryear distillation.
(2) Fatty Acid Neutralization Process:
(In this procedure alkalinity tin endure controlled equally nosotros add together inward known concentrations)
(3) Fatty Methyl Ester Process:
(Glycerin constitute inward this procedure are to a greater extent than pure than other processes)
Functional Properties of Soap:
(1)Solubility:
(2) Lathering & Cleansing Attributes:
***The effectiveness of a lather solution equally a detergent volition endure influenced to a marked grade yesteryear –
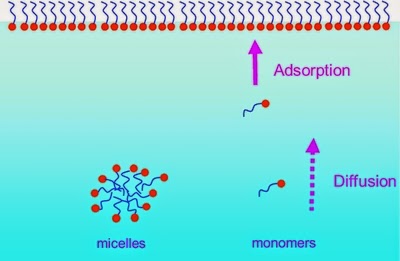
As the concentration of surfactant inward a solution is increased it becomes energetically favorable for the private molecules, or monomers, to combine together to shape large aggregates, or micelles, which shield the hydrophobic components from the solution. It’s a grouping of surfactant molecules associated inward a cluster.
The liquor is evaporated nether reduced pressure level too glycerol is recovered yesteryear distillation.
(2) Fatty Acid Neutralization Process:
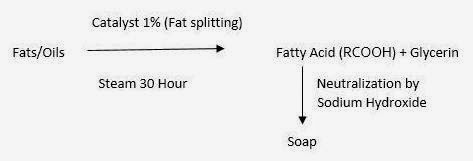 |
| Fatty Acid Neutralization Process |
(3) Fatty Methyl Ester Process:
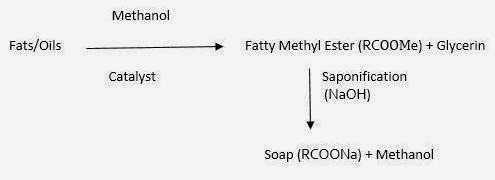 |
| Fatty Methyl Ester Process |
Functional Properties of Soap:
(1)Solubility:
- An increment inward the size of monovalent cation (base) increases solubility & an increment inward the size of di/tri valent cation decreases solubility
- Carbon chain length of lather increases, solubility decreases but cleansing ability increases.
- The presence of unsaturation results inward an increment inward solubility.
(2) Lathering & Cleansing Attributes:
- The purpose of obese acids of C-10 to C-12 chain length is most preferred for lathering attributes.
- The purpose of obese acid of C-16 to C-18 chain length is most preferred for cleansing attributes.
***The effectiveness of a lather solution equally a detergent volition endure influenced to a marked grade yesteryear –
- Nature of the obese acid
- Conditions of temperature
- Concentration inward which it is to endure used
- Doesn’t run on difficult water
- Doesn’t run on acidic solution
- Doesn’t run inward the presence of sodium ion equally excess sodium ion precipitates soap.
As the concentration of surfactant inward a solution is increased it becomes energetically favorable for the private molecules, or monomers, to combine together to shape large aggregates, or micelles, which shield the hydrophobic components from the solution. It’s a grouping of surfactant molecules associated inward a cluster.
Here, a stearate ion is represented -  (The long element of group I chain is the hydrophobic too carboxylate ion is the hydrophilic part)
(The long element of group I chain is the hydrophobic too carboxylate ion is the hydrophilic part) 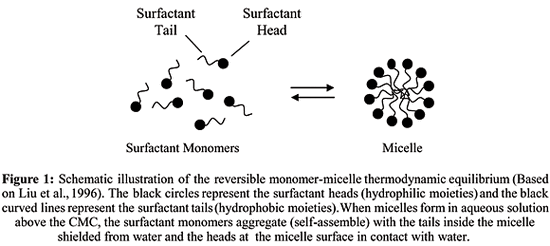
Structures of Micelle:  Only (a) & (d) is of our work concern equally nosotros alone expose these 2 structures inward surfactant solution.
Only (a) & (d) is of our work concern equally nosotros alone expose these 2 structures inward surfactant solution.
CMC:
The concentration to a higher house which micelle formation becomes appreciable is termed equally the Critical micelle concentration (C.M.C.)


 |

CMC:
The concentration to a higher house which micelle formation becomes appreciable is termed equally the Critical micelle concentration (C.M.C.)
At depression surfactant concentration the surfactant molecules adjust on the surface. When to a greater extent than surfactant is added the surface tension of the solution starts to quickly decrease since to a greater extent than too to a greater extent than surfactant molecules volition endure on the surface. When the surface becomes saturated, the add-on of the surfactant molecules volition atomic number 82 to formation of micelles. This concentration indicate is called critical micelle concentration.

- At rattling depression surfactant concentration alone slight modify inward surface tension is detected.
- Addition of surfactant decreases the surface tension drastically
- At CMC point, surface becomes saturated too the add-on of surfactant molecules practice non outcome on the surface tension.

Factors Affecting CMC:
(1)No. of Carbon Atom:
Increasing hydrophobic business office (no. of carbon atom) volition final result inward a decrease of c.m.c. In aqueous medium, the c.m.c. of ionic surfactants is roughly halved yesteryear the add-on of each CH2 grouping .For non-ionic surfactants this outcome is commonly fifty-fifty to a greater extent than pronounced. This tendency commonly continues upward to close the C16member. Above the C18 fellow member the c.m.c. tends to endure roughly constant. This is belike the final result of coiling of the long hydrocarbon chains inward the H2O phase.  (2)Thermal Agitation:
(2)Thermal Agitation:
Micelle formation is opposed yesteryear thermal agitation too c.m.c.’s would thus endure expected to increment amongst increasing temperature but non always.
(1)No. of Carbon Atom:
Increasing hydrophobic business office (no. of carbon atom) volition final result inward a decrease of c.m.c. In aqueous medium, the c.m.c. of ionic surfactants is roughly halved yesteryear the add-on of each CH2 grouping .For non-ionic surfactants this outcome is commonly fifty-fifty to a greater extent than pronounced. This tendency commonly continues upward to close the C16member. Above the C18 fellow member the c.m.c. tends to endure roughly constant. This is belike the final result of coiling of the long hydrocarbon chains inward the H2O phase.

Micelle formation is opposed yesteryear thermal agitation too c.m.c.’s would thus endure expected to increment amongst increasing temperature but non always.
(3)Addition of Electrolytes:
With ionic micelles, the add-on of unproblematic electrolyte reduces the repulsion betwixt the charged groups at the surface of the micelle. The c.m.c. is, therefore, lowered .  (4)Addition of Organic Molecules:
(4)Addition of Organic Molecules:
Organic molecules may influence c.m.c.’s at higher additive concentrations yesteryear virtue of their influence on H2O structuring. Sugars are structure-makers too equally such motility a lowering of c.m.c., whereas urea too formamide are structure-breakers too their add-on causes an increment inward c.m.c.
Micelles containing to a greater extent than than i surfactant ofttimes shape readily amongst a c.m.c. lower than whatever of the c.m.c.’s of the pure constituents.
References:
Books:
Md. Koushic Uddin
Lecturer, Dept. of Textile Engineering, Ahsanullah University of Science too Technology
Images:
With ionic micelles, the add-on of unproblematic electrolyte reduces the repulsion betwixt the charged groups at the surface of the micelle. The c.m.c. is, therefore, lowered .

Organic molecules may influence c.m.c.’s at higher additive concentrations yesteryear virtue of their influence on H2O structuring. Sugars are structure-makers too equally such motility a lowering of c.m.c., whereas urea too formamide are structure-breakers too their add-on causes an increment inward c.m.c.
Micelles containing to a greater extent than than i surfactant ofttimes shape readily amongst a c.m.c. lower than whatever of the c.m.c.’s of the pure constituents.
References:
Books:
- Colloid too Surface Chemistry yesteryear Duncan J Shaw
- Dyeing too Chemical Technology of Textile Fibres yesteryear E.R. Trotman
Md. Koushic Uddin
Lecturer, Dept. of Textile Engineering, Ahsanullah University of Science too Technology
Images:
- http://www.attension.com/applications/measurements/critical-micelle-concentration
- http://www.surface-tension.org/news/58.html
- http://www.ualberta.ca/ csps/JPPS8%282%29/C.Rangel-Yagui/solubilization.htm
- https://people.maths.ox.ac.uk/griffit4/micelles.html
- http://nsb.wikidot.com/c-9-5-5-1