Now You Know How to Measure Fabric Shrinkage in Textile & Apparel Industry
Monday, 21 January 2019
Edit
How to Measure Fabric Shrinkage in Textile & Apparel Industry
Muhammad Ibrahim Khalilullah
Department of Textile Engineering
Daffodil International University
Email: ibrahim23-3123@diu.edu.bd
Department of Textile Engineering
Daffodil International University
Email: ibrahim23-3123@diu.edu.bd
Shrinkage:
The dimensional stability of a fabric is a measure of the extent to which it keeps its original dimensions to its manufacture. Shrinkage is a problem that hampers the dimensional stability of a fabric. A recent survey of manufacturers rated shrinkage as one of the ten leading quality problems. Fabric shrinkage can cause problems in two main areas-
- During garment manufacturing
- During subsequent laundering by the ultimate customer.
i. Relaxation shrinkage:
Relaxation shrinkage is the irreversible dimensional change accompanying the release of fibre strains imparted during manufacture which have been set by the combined effects of time, finishing treatments, and physical restraints within the structure.
ii. Swelling shrinkage:
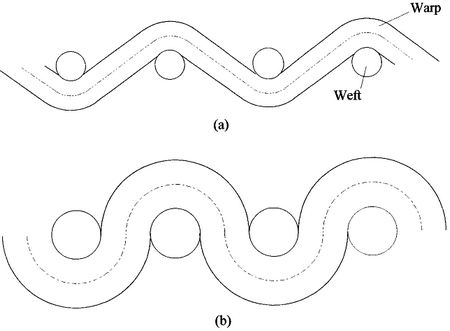 |
| Figure: The effect of swelling of yarn. |
In swelling shrinkage, in a fabric the warp yarn must either increase in length or the weft threads must move closer together.
iii. Felting shrinkage:
Felting shrinkage results from the frictional properties of the component fibres and it causes them to migrate within the structure. This behavior is normally considered for fibres having scales on their surface such as wool.
Wool can be made shrink resistant by treatment. Chlorine treatments removes the scales. Resin treatments are used to mask the scales.
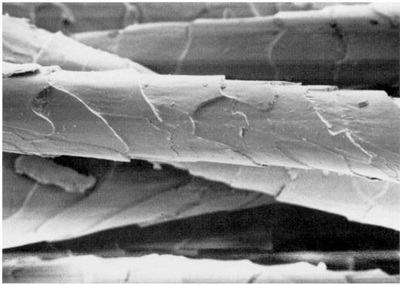 |
| Figure: The scale on wool fibre |
Marking out samples/Preparation of the specimen:
The general procedures for preparing and marking out of samples are given in the British Standard. For critical work the recommended sample size is 500mm X 500mm and for routine work a minimum sample size of 300mm X 300mm is considered as sufficient. The samples are marked with three sets of marks in each direction, a minimum of 350mm apart and at least 50mm from all edges as shown in Figure. In the case of the smaller sample the marks are made 250 mm apart and at a distance of 25 mm from the edge.
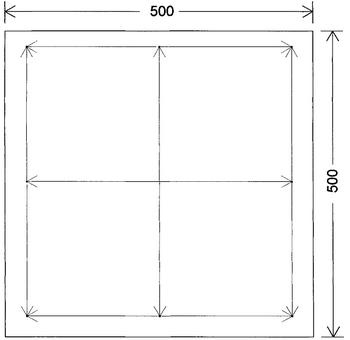 |
| Figure: Marking out of a sample for measuring shrinkage. |
 |
| Fig: Tools of shrinkage measuring |
Working procedure/steps:
Washing: After measurement the samples are washed in the suitable washing solution in a washing machine conforming to certain specification. After the specified time has passed away the sample is rinsed.
 |
| Fig: washing machine |
Conditioning and remeasuring: After drying, the specimen is conditioned in a standard testing atmosphere and the distances between the markings are remeasured.
The percentage dimensional change calculated. The mean dimensional change and direction is reported:
You can also like:
The percentage dimensional change calculated. The mean dimensional change and direction is reported:
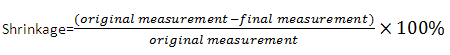 |
- Determination of Tear Strength in Fabrics
- Determination of Tensile Strength in Fabrics
- Procedure of Fabric Seam Slippage Test
- Name of Important Textile Test
- How to Measure Fabric Shrinkage in Textile & Apparel Industry
- Determination of Fabric Abrasion Resistance
- Measuring and Predicting Fabric and Garment Drape
- Determination of Bursting Strength in Fabrics